Drinking Water Quality Testing & Analysis in Laboratory is necessary for Human health. We test Total Coliform Bacteria, Nitrate, pH, Hardness and TDS in Our Lab.
We put a lot of trust when we draw water from tap for a variety of different purposes like drinking, bathing, cooking, etc. Don’t we? We are able to put a lot of trust because we know the water provided to us is treated and tested.
Water testing helps us out to know if the water is safe for usage or not.
What is Water Quality Testing?
Water Quality Testing is a broad description for various procedures used to analyse water quality. Different parameters are analysed for testing the quality of water to ensure if water is safe for usage.
Water testing is just not limited to testing of drinking water. It also plays a major role in testing of domestic waste water, industrial effluents, packaged/natural mineral water, ground water, etc.
Need of Drinking Water Quality Testing and Analysis
We have around 60% water in our body. i.e 2/3 rd part of human body made up of water. what if the water we are drinking is contaminated? Over 3 million people die (majorly because of Diarrhea) every year because of water pollution. To make sure that water we are drinking is pure and contains no bacteria and harmful metals Drinking water analysis in Laboratory is necessary. We have heard Precaution is better than cure since our childhood it is true in this case also.
Let’s imagine a scenario where water sent to us is not being tested. It may happen that the water might contain biological contaminants which may cause health problems.
Or
Let’s imagine another scenario where water discharged from industries is directly released into open sources of water without being tested. It may happen the water being discharged has high levels of Chromium, Nitrates, Phosphates or biological contaminants which can have a serious impact on aquatic ecosystem leading to its destruction.
This helps us understand the level of threat that lies if water is used or discharged without testing? Regular practice of water testing rules out the chances of suffering from health problems and also gives us a chance to protect our precious environment.
Location of Drinking Water Sampling Points
Drinking water Sampling is most important process in Drinking water analysis. it must be taken from location that is representative of water source to be tested.
Sampling Frequency
The Most important test in water quality surveillance are those for microbiological quality i.e. indicator of bacteria, Turbidity, Free chlorine, pH. These should be carried out whenever a sample is taken. It is recommended that Drinking water analysis to be carried out once in a year.
Storage of Samples
Although recommendation varies, the time between sample collection & analysis should, in general not exceed 6 hours & 24 Hours is considered the absolute Maximum. It is assumed that the samples are immediately placed in a light proof insulated box containing melting ice or ice packs with rapid cooling. If ice is not available, the transportation time must not exceed 2 hours before drinking water analysis.
Having understood the importance of testing water quality, the next question arises is how to test water quality.
Drinking Water Quality Testing and Analysis
For water quality testing it is necessary to first understand the purpose; where the water is going. Will it be used for drinking purposes or will the water be discharged into open sources. Once this is known then the standards and parameters which need to be analysed should be understood.
- Standards
Some of the standards which are usually referred during Analysis of Water quality are of APHA, IS, CPCB and WHO. Depending upon the purpose, the set of standards can be referred.
- Types of tests
Water testing can be grouped into three major categories.
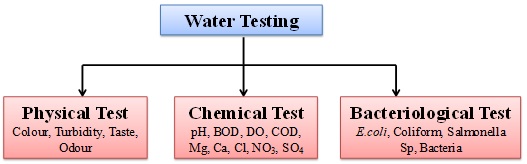
- Physical Tests For Water Quality – These indicate properties which are detectable by senses.Colour, Turbidity, Odour and Taste, these parameters are grouped under physical tests.
- Chemical Tests for Water Quality – These determine the amount of mineral and organic substances that affect the quality of water. pH, BOD, DO, Ca, Mg, Cl are some of the parameters which are grouped under chemical tests.
- Bacteriological Tests for Water Quality – These indicate the presence of bacteria. Bacteriological tests are used primarily as an indicator of faecal contamination.
Water Quality Testing Procedures involve a series of steps to assess the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water in order to determine its safety and suitability for various purposes.
Sampling Methods for Physio-Chemical Analysis In Laboratory

Result of physio-chemical analysis is of no value if the sample tested are not properly collected & stored. In general, Time between sampling & analysis should be kept to a minimum. Storage in a glass or polyethylene bottles at low temperature (e.g. 4 DegC) in the dark is recommended. pH, Turbidity & Residual chlorine should be tested immediately after sampling as they will chance during storage & transportation.
Physico-Chemical Analysis in Laboratory
Chlorine residual
The disinfection of drinking-water supplies constitutes an important barrier against waterborne diseases. Although various disinfectants may be used, chlorine in one form or another is the principal disinfecting agent employed in small communities in most countries. Three types of chlorine residual may be measured: free chlorine (the most reactive species, i.e. hypochlorous acid and the hypochlorite ion); combined chlorine (less reactive but more persistent species formed by the reaction of free chlorine species with organic material and ammonia); and total chlorine (the sum of the free and combined chlorine residuals).
pH
Portable pH electrodes and meters are available. If these are used in the laboratory, they must be calibrated against fresh pH standards at least daily; for field use, they should be calibrated immediately before each test. Results may be inaccurate if the water has a low buffering capacity and it will not serve the purpose of drinking water analysys.
Turbidity
In all processes in which disinfection is used, the turbidity must always be low—preferably below 1 NTU. It is recommended that, for water to be disinfected, the turbidity should be consistently less than 5 NTU.
Color
If Drinking water is colored then may be colored organic matter, e.g. humic substances, metals such as iron and manganese, or highly colored industrial wastes are present. Drinking-water should be colorless.
Taste and odor
Odors in water are caused mainly by the presence of organic substances. Some odors are indicative of increased biological activity, others may result from industrial pollution. Generally, the taste buds in the oral cavity detect the inorganic compounds of metals such as magnesium, calcium, sodium, copper, iron, and zinc. As water should be free of objectionable taste and odor, it should not be offensive to the majority of the consumers.
Drinking Water Quality Testing Parameters and Standards to be checked in Laboratory
Water is a vital natural resource which is essential for multiplicity of purpose. Drinking water quality standards describes the quality parameters set for drinking water. Drinking water or potable water is water safe enough to be consumed by humans. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry meets drinking water quality standards, even though only a very small proportion is actually consumed or used in food preparation. Typical uses (for other than potable purposes) include toilet flushing, washing and landscape irrigation.
As Per Indian Standard Specifications For Drinking Water Quality standards:
| S.NO. | Parameter | Requirement desirable Limit | Remark |
| 1 | Color | 5 | May be extended up to 50 if toxic substances are suspected |
| 2 | Turbidity | 10 | May be relaxed up to 25 in the absence of alternate |
| 3 | pH | 6.5 to 8.5 | May be relaxed up to 9.2 in the absence |
| 4 | Total Hardness | 300 | May be extended up to 600 |
| 5 | Calcium as Ca | 75 | May be extended up to 200 |
| 6 | Magnesium as Mg | 30 | May be extended up to 100 |
| 7 | Copper as Cu | 0.05 | May be relaxed up to 1.5 |
| 8 | Iron | 0.3 | May be extended up to 1 |
| 9 | Manganese | 0.1 | May be extended up to 0.5 |
| 10 | Chlorides | 250 | May be extended up to 1000 |
| 11 | Sulphates | 150 | May be extended up to 400 |
| 12 | Nitrates | 45 | No relaxation |
| 13 | Fluoride | 0.6 to 1.2 | If the limit is below 0.6 water should be rejected, Max. Limit is extended to 1.5 |
| 14 | Phenols | 0.001 | May be relaxed up to 0.002 |
| 15 | Mercury | 0.001 | No relaxation |
| 16 | Cadmium | 0.01 | No relaxation |
| 17 | Selenium | 0.01 | No relaxation |
| 18 | Arsenic | 0.05 | No relaxation |
| 19 | Cyanide | 0.05 | No relaxation |
| 20 | Lead | 0.1 | No relaxation |
| 21 | Zinc | 5.0 | May be extended up to 10.0 |
| 22 | Chromium as Cr +6 | 0.05 | No relaxation |
Water Quality Testing Parameters
Here is a list of water quality testing parameters and the Water quality testing methods which are used to analyse the quality of water:
| Sr No | Water Testing & AnalysisParameter | Water Testing and Analysis Method |
| 1 | Colour | Visual comparison, Spectrophotmetric method |
| 2 | pH | pH paper, Universal indicator or pH meter |
| 3 | Turbidity | Nephelometric method |
| 4 | Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | Winkler method |
| 5 | Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) | Winkler method |
| 6 | Chloride (Cl) | Argentometric method |
| 7 | Hardness – Ca and Mg | EDTA method |
| 8 | Total Dissolved solids | Gravimetric method |
| 9 | Sulphate as SO4 | Turbidimetric method |
| 10 | Nitrate as NO3 | Colorimetric method |
| 11 | Iron (Fe) | AAS |
| 12 | Sodium (Na) | AAS |
| 13 | E.Coli | MPN – completed test for E.coli |
| 14 | Total Coliform Bacteria | MPN |
| 15 | Total Bacteria | Enumeration method |
These are some of the common parameters analysed to test the water quality and on comparison with the standards an overall idea of the quality of water can be achieved.
The testing of water can be done by hiring professional or by using test kits at home. The water testing kits can be used and the results can be sent to a professional for analysis. He will analyse and provide you the results with recommendations if needed.
Read more about Surface Water Monitoring
Frequently Asked Questions:
To analyse the quality of drinking water Total Coliform Bacteria, Nitrate-nitrogen, pH, Iron, Hardness (CaCO3), Sulphates, Chlorides and specific conductance tests can be performed.
Water test results should be analysed with care. For each parameter, results need to be in pre-defined limits. If any parameter is exceeding its limit then that water should not be used for drinking.
For drinking water Total Coliform Bacteria, Nitrate nitrogen, pH, Iron, Hardness CaCO3, Sulphates, Chlorides and specific conductance are the tests used commonly.
dissolved oxygen, pH, temperature, salinity and nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) are the 5 water quality tests. These are also called as 5 Main indicators of water quality testing.
Water Quality Testing & Analysis Laboratory
We Perfect Pollucon Services as Environmental Consultant have highly Qualified and Experienced Experts to do Drinking water Analysis. We already provide these services to major industries to small Villages like in Mumbai, Thane, Navi Mumbai, Palghar, Panvel.
If you want to avail our services or to know more about our services please fill contact form mentioned on right hand side.
how to carry out Air Quality Monitoring and Ambient Air quality Standards by Pollution Control Board.
Learn more about Noise level Survey and Limits by Pollution control boards


