How to Reduce Particulate Matter?
We can reduce particulate matter by reducing usage of particulate mater forming appliances, Avoid burning, quit indoor smoking, walk instead of vehicle, using solar energy, regular maintaining vehicle etc.
Particulate matter is one of the most important and dangerous air pollutant present in the air along with harmful gases, chemicals, smoke particles, etc. Air quality is determined by studying air pollutants present in air which is called as Air Quality Testing.
It can be affected by amount of air pollutants present in atmosphere, weather, temperature etc.
Indoor Particulate Matter
Indoor particulate matter refers to the presence of solid or liquid particles suspended in the air within enclosed spaces, such as homes, offices, schools, and other indoor environments. These particles can originate from various sources, including cooking activities, smoking, cleaning products, dust mites, pet dander, and outdoor pollutants that infiltrate indoors.
Exposure to indoor particulate matter can have adverse health effects, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma or allergies. It is important to address indoor particulate matter through effective ventilation, regular cleaning and dusting, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, minimizing the use of harsh chemicals, and adopting practices that reduce particle generation, such as proper cooking ventilation and smoking cessation.
By reducing indoor particulate matter levels, we can create healthier and more comfortable indoor environments for occupants.
How To Reduce Particulate Matter?
- We can reduce the usage of Household products which create particulate matter
- Not to burn wood, leaves or any yard waste

- Stop smoking especially indoor

- Diesel vehicles are major source of particle pollution, it can be reduced by replacing older engines with new engines
- Walk, cycle or use public transport or share vehicle wherever possible
- Pay attention to your maintenance of your vehicle to reduce particulate matter
- Use Indoor Air purifiers to reduce particulate matter in homes and offices
- Conserve energy by using solar energy, bio-gas, rainwater harvesting etc. to control pollution from particulate matter

Together we can reduce Particle pollution to make Earth better place for next generation.
Also you will like How to reduce air pollution from factories.
What is Particulate matter?
Particulate matter (PM) refers to small and medium solid or liquid particles present is atmosphere. Particulate matter is consists of organic chemicals, metals, soil and dust also.
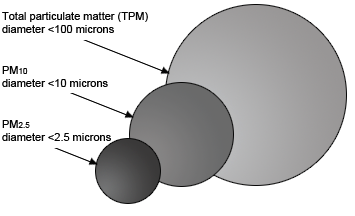
Smaller the particle it is more hazardous, as it can go deeper in lungs which has diameter less than 2.5 micrometers. Particles between 2.5 to 10 micrometers are less harmful as they tend to stay in nose and throat.
What does PM10 Mean?
PM10 is Particulate matter particles having size between 2.5 to 10 micrometer. (imagine 25 to 100 times thinner than human hair.) We call it as PM10 means Particulate Matter upto 10 micrometers in size. PM10 are less harmful than PM2.5 because their larger size they cannot travel farther and can not go deep into lungs.
You will also like to read about Sources and Types of Indoor air pollution
What causes Particle Pollution?
Any type of burning or combustion leads to particle pollution. It can be also generated during construction, unpaved roads, fields etc.
Also these particles emitted from automobiles, industries and tobacco smoke etc.
How dangerous is Particulate Matter to us?
Particulate matter are considered as greatest concern causing human health problems. As mentioned before small particles i.e. less as 2.5 micrometers can go to our lungs and some may get into our bloodstream.
Long term exposure to particulate matter invites heart and lung problems. Also studies have shown that it harms most likely to children and older adults.
Particulate Matter Effects
Particulate matter exposure can be linked to below mentioned health issues:
- Increased respiratory symptoms such as difficulty in breathing, coughing and irritation etc.
- Decreased lung capacity
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Asthma
- Heartbeat irregularization
- Heart attacks
- And Most importantly Premature Death
Particulate matter, also known as PM, refers to a mixture of solid and liquid particles suspended in the air. These particles can vary in size, ranging from large visible particles to smaller particles that are not visible to the naked eye.
When inhaled, particulate matter can have detrimental effects on human health. The health impacts depend on the size of the particles, with smaller particles (PM2.5 and PM10) posing a greater risk. Exposure to particulate matter can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
It can also exacerbate existing respiratory conditions such as asthma and increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Long-term exposure to high levels of particulate matter has been linked to respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses, reduced lung function, and even premature death.
Additionally, particulate matter can have environmental effects, including visibility reduction, damage to ecosystems, and contribution to climate change. It is crucial to reduce particulate matter emissions and take measures to protect individuals and the environment from the harmful effects of this air pollutant.
Do you Know How to Measure Particulate matter in Atmosphere?
Reduced Visibility due to particulate matter:

They can reduce Visibility when they are present in atmosphere in large quantity.
Other Hazards
They can be carried over long distance and settling on wrong surface such as lakes, forests, crops, Soil, stones can prone to damage. E.g. acid rains
Particulate Emission Control
Particulate emission control is a critical aspect of environmental management aimed at reducing the release of solid or liquid particles into the atmosphere. It involves implementing various strategies and technologies to mitigate the adverse effects of particulate matter on human health and the environment.
Source control measures focus on minimizing particulate emissions at their origin, while emission control technologies such as filtration systems, electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers, and catalytic converters help capture and remove particulate matter from industrial processes and vehicle exhaust.
Regular monitoring and compliance with emission standards ensure that particulate emissions are effectively controlled, leading to cleaner air and a healthier environment for all.
For more on Particulate Emission Control please refer to below PDF
Share this Article with your friends:
Read More Environmental Monitoring and Assessment
Learn More about Environmental Monitoring Techniques
1. Improve ventilation by opening windows or using exhaust fans to allow fresh air circulation.
2. Use air purifiers with HEPA filters to capture and remove particulate matter from indoor air.
3. Regularly clean surfaces, dust, and vacuum with a HEPA filter to minimize settled particulate matter.
4. Avoid smoking indoors to prevent the release of particulate matter.
5. Control humidity levels to prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which can release particulate matter.
6. Minimize the use of products that generate particulate matter, such as candles and certain cleaning products.
7. Keep outdoor pollutants out by using doormats and removing shoes before entering the house.
8. Regularly maintain HVAC systems and replace air filters to prevent the circulation of particulate matter.
9. Ensure proper ventilation during activities that generate particulate matter, such as cooking or using fireplaces.
10. Consider incorporating indoor air-purifying plants, such as spider plants or peace lilies, to help filter the air and reduce particulate matter.
1. Implementing strict emissions standards and regulations for industries and vehicles.
2. Using advanced filtration systems and air pollution control technologies.
3. Promoting sustainable agricultural practices to reduce dust and soil erosion.
4. Encouraging the use of cleaner fuels and energy sources.
5. Implementing effective dust control measures in construction sites and mining areas.
6. Educating the public about the importance of reducing individual contributions to particulate pollution.
7. Monitoring air quality and taking prompt action to address high pollution levels.
8. Investing in research and innovation for developing new technologies to control particulate pollution.
9. Collaborating with international organizations and governments to address transboundary particulate pollution.
10. Encouraging sustainable urban planning and transportation strategies to reduce traffic-related particulate pollution.


