Noise Level Measurement Procedure
Noise Level Measurement Procedure
Noise level measurement procedures are followed while monitoring sound level or acoustic energy level in the specified area. We will see what are important factors to keep in mind while measuring noise level.
These days annoying noise levels have started to become a major threat to public health. Noise in simple terms can be defined as unwanted or unpleasant sound which disturbs the environment and has a significant impact on the quality of life.
Yes! Exposure to continuous high noise levels can seriously jeopardize our quality of life.
We all very well know how exposure to high noise level can result in hearing impairment, headache, sleep disturbance and impaired task performance.
But, wait there is more.
Recent studies have shown, continuous exposure to high noise levels can result in
- Indigestion
- Peptic ulcer
- Hypertension
- Fatigue
- Hearing loss in new borns
- Prematurity, intrauterine growth retardation and disruption to normal growth and development of premature infant.
Now that we have got a slight idea of the effects long term exposure to noise can have on us, we can very well understand the importance to monitor noise pollution and try some control measures to minimize it.
The major step of noise level monitoring or rather any monitoring is measurement of pollutants.
For easy understanding of noise level measurement procedure we can follow the below mentioned simple steps.

Let’s first try to understand what are noise waves?
- Noise waves or acoustic waves are emitted from specific items or machinery
- Generally sound energy radiation pattern is isotropic i.e. it spreads in all direction.
- In most of the cases sound transmits through air in straight line
- Noise level are measured using noise level meter that provides various options for signal averaging and analysis points
- Main concern of noise level on human is it directly affects sleep, relaxation and conversion
Read More about Noise Mapping
Prerequisites for Noise Level Measurement Procedure
Measurement of Noise from One Source
The measurement of noise from a stationary source is carried out near the source where sound pressure is higher from the source compared to all other noise. The sound measured nearby the source tells the noise generated by the source.
Measurement of Noise for varying noise levels
If the amplitude of the noise level from source is varying with time, then suitable averaging technique or statistics which yield an appropriate measurement of noise is required. There are several alternatives can be selected to decide appropriate techniques.
If the sound level of the source is varying then the overall sound levels will be controlled by loud sound levels. Whenever there is a variation in noises then Leq method is used for measurement. Leq method is used to give higher weightage to louder noises by applying logarithmic averages.
To measure loud noises impulse noise level measurement Procedure is used. Noise level meters with sound pressure averaged for 35 ms are used for impulse noise level measurement. Non-impulsive measurement required noise level meters with the fast or slow averaging method. For fast averaging method time constant of 125 ms is set and for a slow averaging method, 1000 ms time is set in noise level meters.
Sound Pressure level or Sound Power level
Sound level measured from specific distance from sound source can be used to calculate sound power output. Similarly, Sound power of the source can be used to calculate pressure level for the sound at other locations away from the source. Sound pressure level or power levels are used in cases where measurement of sound level is difficult due to the presence of other loud noises.
Learn more about Noise Mapping Procedure
Noise Weakening with distance from noise source
The relation between sound power at source and sound power at particular distance from the source is influenced by multiple physical factors. The major factors in influencing the sound over the distance are source-receptor distance, topography of that area and ground level characteristics and meteorological conditions.
Noise Level measurement Procedure
Identification of location and its type and instrument
The first step before starting measurement of noise level is to always identify the type of location.
Location to be monitored could belong to any of the five areas, viz. Commercial, Industrial, Residential, silent and mixed.
This must be identified. Once we are able to identify the type, we can then select a position to place the instrument.
The instrument must always be positioned away from direct source, vibration and from any obstruction. This is because we are performing ambient noise monitoring.
Selection of Noise Measurement Instrument, Sampling Duration and Scale
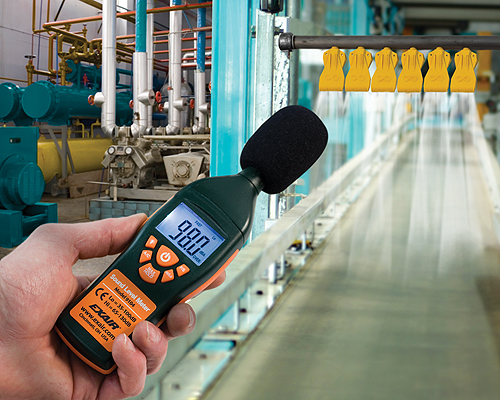
To measure noise level, the most extensively used instrument is a Sound Level Meter (SLM) which commonly is known as a noise meter.
After selection of instrument, selection of sampling duration and scale is must. With these it is also necessary to consider the parameters which we need to measure like;
Lmax, Lmin, Leq, etc

Comparison with Noise standards
Once we get the monitoring records then we can compare them with standards to understand if noise levels are exceeding the standards and if they are then by how much.
In India, we use standards prescribed by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
Noise level Measurement Standards
The below table shows the Noise level Monitoring standards prescribed by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
| Area code | Category of area/Zone | Limits in db (A) | |
| Day Time | Night Time | ||
| (A) | Industrial area | 75 | 70 |
| (B) | Commercial area | 65 | 55 |
| (C) | Residential area | 55 | 45 |
| (D) | Silence zone | 50 | 40 |
Now, we would easily get an idea about noise level in the area we would monitor.
Once, we completely analyse these the next question comes is how to control and bring down the noise levels which are exceeding the permissible levels.
Read more about How to measure noise level measurement at office?
The answer to this question is below:
- Control measures
Any Noise level monitoring or measurement procedure is complete only after the results are analysed and remedies are suggested to bring down the pollution if any.
To minimize the noise levels some simple steps which one can follow at individual levels are;
- Eliminate the source: Once the source is identified, we can try to eliminate the use of it completely.
- Substitution: If removal of pollutant source if not possible, then we can try for substitution of it with the less noise-producing source.
- Isolation: If the above two are not possible, one can try to either isolate the pollutant source or himself from it. For this one can make use of double panelled windows, acoustical tiles, etc.
- If any of the above methods are not effective in lowering noise levels, then one can opt for PPE (Personnel Protective Equipments) like ear muffs, cotton balls, etc.
Learn more about Noise Monitoring Guidelines by CPCB
How do you Measure Noise Level in the Workplace?
Measuring noise levels in the workplace involves using a sound level meter, a device designed to quantify the intensity of sound. The process typically begins by selecting a suitable sound level meter and calibrating it to ensure accuracy.
Measurement locations are then chosen, considering areas near machinery or workstations that are potential sources of noise. The sound level meter is positioned at these locations and measurements are taken, considering factors like height and distance from the noise source.
The duration and locations of measurements are monitored, and data is recorded and analyzed to assess compliance with noise exposure limits and identify areas that require noise control measures.
Adhering to local regulations and guidelines is essential in conducting accurate and meaningful noise level assessments in the workplace.
Noise Measurement Chart
A noise measurement chart provides a reference for understanding sound levels in decibels (dB) and their impact on hearing and comfort. For instance, a quiet library typically measures around 30 dB, normal conversation ranges from 50-60 dB, and traffic noise or a busy office can reach 70-80 dB.
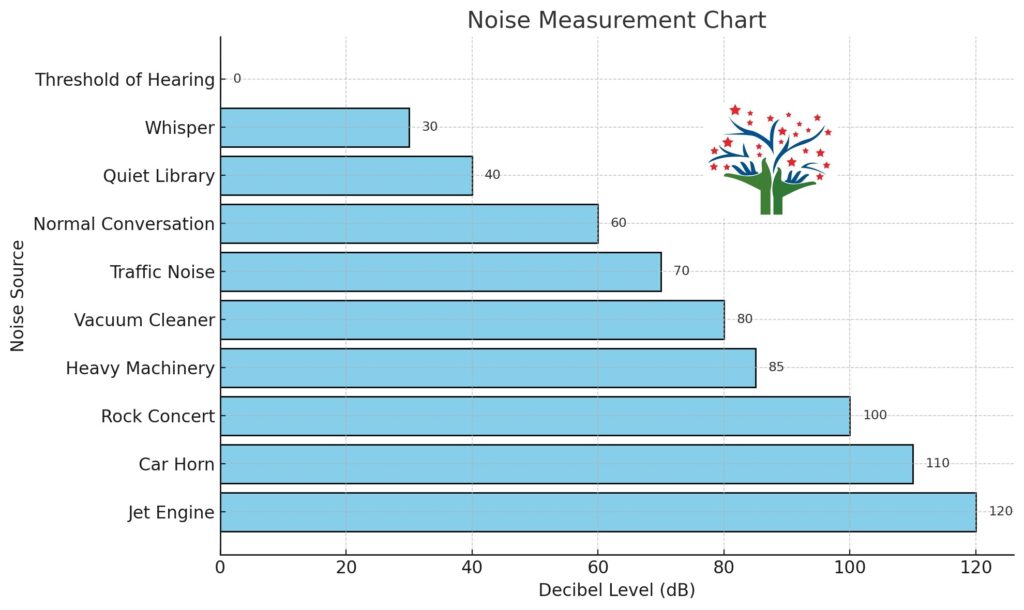
Sounds above 85 dB, like heavy machinery or loud music, are considered potentially harmful with prolonged exposure, while levels above 120 dB, such as a rock concert or a jet engine, can cause immediate hearing damage. These charts are essential for identifying safe noise levels and implementing effective noise control measures.
Also Read more about How to Reduce Noise level at Homes and office
Noise Measurement Calculator
A noise measurement calculator is a tool used to quantify sound levels in a specific environment. It typically measures noise in decibels (dB), a unit that expresses the intensity of sound. The calculator may take inputs such as the distance from the noise source, sound pressure level, and other environmental factors that could influence sound propagation.
Check Out our Noise level Measurement Calculator:
It can be used in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and environmental monitoring, to assess whether noise levels are within acceptable limits for health, safety, or regulatory compliance. Some advanced calculators may even factor in frequency weighting curves, such as A-weighting or C-weighting, to adjust measurements based on human hearing sensitivity.
Noise Level Measurement Procedure PDF by Perfect Pollucon Services
The noise level measurement procedure involves using a sound level meter to accurately assess the intensity of sound in a specific environment. The process includes selecting the appropriate equipment, positioning the microphone, and recording data over a defined period. The results are then analyzed to ensure compliance with noise regulations and to identify areas for potential noise reduction.
Noise pollution can have a huge impact on our environment and quality of life. But to acquire a better and healthy life one simple thing we all can do is to remember to try to make less noise when we can, not only for our own sake but also for the sake of those who are around you!
Share this article with your Friends and family !
Noise is typically measured using a sound level meter that captures sound pressure levels and converts them into decibels (dB), a logarithmic unit of measurement. Measurements consider factors like frequency, duration, and intensity, often using A-weighting (dBA) to mimic human hearing sensitivity. Advanced methods may also include spectral analysis to evaluate noise characteristics across different frequencies.
A normal noise level depends on the environment:
For indoor spaces like homes or offices, typical noise levels range between 30-50 decibels (dB), which is considered quiet to moderate.
For outdoor environments, normal levels range from 50-60 dB, such as in residential areas during the day.
Noise above 85 dB (e.g., traffic, machinery) can be harmful to hearing with prolonged exposure.
Standards may vary depending on local regulations and specific environments.
Noise is measured in decibels (dB), a logarithmic unit that quantifies sound intensity. For human hearing, A-weighted decibels (dBA) are commonly used to account for the ear’s sensitivity to different frequencies.
Yes, you can use your phone as a dB meter by installing sound level meter apps, which utilize the phone’s microphone to measure noise levels. While they provide a general estimate, they may not be as accurate as professional sound level meters due to microphone limitations.
Noise is calculated by measuring sound pressure levels (SPL) using a sound level meter, which records fluctuations in air pressure caused by sound waves. The measurements are expressed in decibels (dB), calculated on a logarithmic scale relative to a reference level, typically 20μPa the threshold of human hearing. Adjustments like A-weighting (dBA) are often applied to align the readings with human hearing sensitivity across frequencies.
The unit of sound is the decibel (dB), which measures the intensity or loudness of sound. It is a logarithmic unit that compares the sound pressure of a noise source to a reference level, typically 20μPa the threshold of human hearing.
The best noise level for comfort and health is typically below 35 dB in indoor environments like homes and offices, as recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). For sleeping areas, a noise level of 30 dB or less is ideal to ensure restful sleep.
To test dB levels, use a sound level meter or a mobile app that utilizes the device’s microphone to measure sound pressure levels in decibels (dB). Position the device at ear level in the area being tested, away from obstructions, for accurate readings.
dB (decibel) is a unit used to measure the intensity or loudness of sound on a logarithmic scale. It quantifies sound pressure relative to a reference level, typically the threshold of human hearing at 20μPa
Sound level refers to the intensity of sound in a specific environment, measured in decibels (dB). It indicates the pressure exerted by sound waves and can range from very quiet levels (e.g., 30 dB in a library) to loud and potentially harmful levels (e.g., 120 dB at a rock concert).
The best method to reduce noise pollution is to use soundproofing techniques, such as installing acoustic panels, double-glazed windows, and dense vegetation as barriers. Additionally, implementing stricter regulations on noise levels in urban and industrial areas can significantly minimize noise pollution.
The decibel (dB) unit of noise measures sound intensity on a logarithmic scale. Noise levels are often expressed in A-weighted decibels (dBA) to reflect human hearing sensitivity across different frequencies.
Noise levels below 70 dB are generally considered safe for prolonged exposure, as they are unlikely to cause hearing damage. However, exposure to levels above 85 dB for extended periods can be harmful and may require hearing protection.
A fan operating at 60 dB is moderately loud, comparable to the noise level of a normal conversation. While it’s not harmful, it might feel intrusive in quiet environments, especially during activities like reading or sleeping. Fans below 50 dB are generally considered quieter and more comfortable.


I live in a High Rise unit fronting the Main Road to Surfers Paradise. General traffic noise is not a problem, however the Decibels put out from noisy motorbikes and some cars can be very disturbing. I have recorded on my iPad readings in excess of 125 decibels.
My location is approx 100 Meters back from the Highway and on level 8 of a 22 level high rise. This building is located at a Traffic Light controlled Junction which is the contributing factor. Both Motor Bikes and performance enhanced cars plus excessive speed and accelerating from the traffic lights is generally the cause.
Yes Alan,
We understand it. noise from some cars and bikes can be very disturbing. It can be tackled by using some noise proof glasses for sliding windows to reduce effects.
Hope this helps you. Thanks