How to Measure Noise in Workplace
Perfect Pollucon Services, with over 25 years of experience in environmental monitoring, has been helping industries maintain safe noise levels in the workplace.
Noise pollution is a major occupational hazard, and monitoring it correctly is critical for employee health and regulatory compliance. This article will guide you through the process of measuring noise levels, understanding industry standards, and ensuring compliance with workplace safety norms.
What is Noise?
Noise is any unwanted or harmful sound that can cause discomfort, interfere with communication, or pose serious health risks such as hearing loss and stress-related illnesses.
In industrial settings, noise can originate from heavy machinery, equipment operations, or even workplace layouts that amplify sound. Long-term exposure to high noise levels can lead to occupational hearing loss, reduced productivity, and regulatory violations if not managed properly.
Why measure noise in Workplace?
Noise level measurement plays important role in workplace hearing conversion. It helps to identify high noise zones in workplace and employees who may get affected. Required action be taken based on observations from noise measurement.
Common Mistakes in Workplace Noise Measurement
Over our 25+ years in environmental monitoring, we’ve observed some common mistakes that companies make while measuring workplace noise:
- Relying on a single measurement: Noise levels fluctuate throughout the day. A one-time reading may not reflect actual exposure.
- Using incorrect equipment: Not all sound level meters (SLMs) are suitable for industrial monitoring. Choosing the wrong type (e.g., below Type 2 accuracy) can lead to unreliable data.
- Ignoring impulse or intermittent noise: Sudden loud noises from machines (e.g., metal stamping, hammering) can be more damaging than continuous noise but are often overlooked in standard measurements.
- Not considering worker movement: If employees move between different noise zones, a noise dosimeter is required instead of a fixed-point measurement.
- Skipping calibration: An uncalibrated noise level meter can provide misleading results. Calibration should be done before and after measurements.
How to Find Noise problems at the Workplace?
To identify noise level problem in workplace readings can be taken from noise level meter at different locations or sites in company premises.

At initial stage a simple walk may guide and gives idea about noise issues in premises.
Below are the possible indicators of high noise areas:
- Noise is louder that city traffic
- Employees have to speak loudly with each other within distance of 3 feet
- After working for years employees developed hearing loss
- After end of the day people have developed temporary hearing loss as they have to increase volume of radios or TVs
- They hear temporary ringing or humming in their ears when leave work
How to Plan Noise level Measurement?
Before reading “How to Measure noise level in workplace” making plan for noise level measurement is important to know what type of information is required.
- Purpose of Noise measurement: Noise rules, Hearing loss anticipation, noise control etc.
- To know about source of high noises
- The existence pattern of noise: continuous, variable, irregular, impulse etc.
- Exposed persons
Noise dosimetry is recommended when noise levels vary throughout the day or employees are fairly mobile in premises.
Read More about Noise Level Testing & Monitoring
What is Sound level Meter (SLM)?
Types of Noise Measurement Devices & Their Best Uses
1️⃣ Sound Level Meters (SLMs): Used for spot measurements in fixed locations. Best for environments with consistent noise levels.
2️⃣ Noise Dosimeters: Recommended when noise exposure varies throughout the workday or employees move between noise zones. It provides a more accurate cumulative exposure assessment.
3️⃣ Octave Band Analyzers: Used for more advanced noise frequency analysis, useful in engineering noise control.
Microphone detects and reads minimal air pressure changes and convert them into electric signals. These signals are processed by electric circuits and converted into decibels. SLM can read noise level for one location at a time.
While measuring noise levels it is held in an arm’s length at the ear height. It does not matter whether microphone is pointe towards source. Sound level monitor must be calibrated before and after use.
Every sound level meter has two modes and those are SLOW and FAST. It is the response rate which SLM averages before showing on screen. For workplace noise level monitoring it should be taken as SLOW.
Type 2 noise level meters are adequately accurate. Type 1 are expensive, Highly Accurate and used in laboratories, engineering etc. Any Noise level meter less accurate than type 2 should not be used for workplace Sound measurement.
When Windshield should be used?
When air blows by microphone, readings are altered. To avoid effect of wind, it recommended to cover microphone by windshield. Its cover is made up of sponge.
What is Noise Survey & How to Conduct It?
A noise level survey is the process of noise measurements throughout the plant or premises of the organization. It may provide useful information like:
- Areas where employees exposed to high noise levels
- Machines or instruments which generates high level of noise
- Employees exposed toharmful noise levels
- Noise control options to reduce exposure to noise
Now we will see how to conduct a noise Survey:
Planning a Noise Level Assessment: Key Factors to Consider
A well-structured noise assessment plan ensures accurate results and compliance with workplace safety standards. Based on our 25+ years of experience, here’s what companies should consider:
✅ Purpose of Noise Measurement: Regulatory compliance (OSHA, Indian Noise Standards), hearing loss prevention, or noise control planning.
✅ Source Identification: Identifying machines or activities producing hazardous noise levels.
✅ Noise Patterns: Is it continuous, variable, impulsive, or intermittent? This helps determine whether a standard sound level meter or a noise dosimeter is needed.
✅ Employee Exposure: Understanding which workers are at the highest risk.
✅ Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to workplace noise exposure limits set by organizations like OSHA, CPCB (India), and ISO 1999:2013.
How to measure noise in Workplace?
Noise level survey is conducted in areas where hazardous noise levels are present. It is the process of Noise level measurement at selected locations in entire organization premises. Measurement of noise level is carried out by noise level meter.
In this process a rough diagram of factory plant is drawn on a paper showing locations of sources and employees. Sound measurements are taken for number of suitable locations and marked on the sketch. The higher the number of measurements taken, the more accurate survey is.
A noise map can be produced drawing lines between points of equal sound levels.
It provides very useful information as shown in below image:
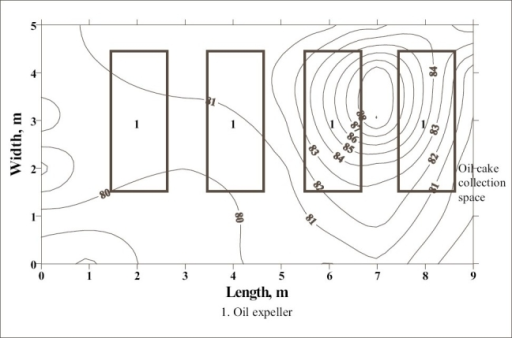
When Purpose of Noise level survey is for hearing loss then microphone should be placed as close as location of ears of employee. Any shield between source and microphone of noise level meter should be avoided. For employee noise level meter needs to be held within 0.5 meters of employee’s shoulder.
Above method works best if noise levels are in category of Continuous noise level. If noise level is type of impulse, intermittent and variable then it becomes difficult to determine average exposure to noise by noise level meter and that is when noise dosimeter comes into picture.
One of the most effective ways to visualize workplace noise is by creating a Noise Map. Here’s how:
- Mark key noise sources (machines, processes, workstations) on a floor plan.
- Take multiple noise level readings and plot them on the map.
- Draw contours connecting equal noise level zones (similar to a weather heatmap).
- Identify areas exceeding 85 dB(A) (OSHA’s permissible exposure limit) and plan noise control measures accordingly.
Workplace Noise Regulations & Compliance
Employers must adhere to workplace noise standards set by OSHA (USA), CPCB (India), and international guidelines (ISO 1999:2013).
- OSHA Noise Standard (29 CFR 1910.95): Limits exposure to 90 dB(A) for 8 hours and mandates hearing protection above 85 dB(A).
- CPCB (India) Noise Limits: Workplace noise should not exceed 75 dB(A) in industrial zones and 55 dB(A) in commercial zones.
- ISO 1999:2013: Specifies methods to estimate long-term noise exposure risks.
Failure to comply can lead to penalties, employee lawsuits, and productivity losses.
This Article Is written by Perfect Pollucon Services Environmental Monitoring Service Provider company in India offer Environmental monitoring Services.
Noise levels can be measured using Sound Level Meters (SLMs) for spot checks or Noise Dosimeters for cumulative exposure. The readings should be compared to OSHA or CPCB standards.
OSHA allows up to 90 dB(A) for 8 hours, while CPCB sets 75 dB(A) for industrial areas. Higher levels require hearing protection or noise control measures.
Prolonged exposure to 85 dB(A) or more can cause hearing loss, increased stress, lower productivity, and higher accident risks due to communication difficulties.
Use a Type 2 Sound Level Meter, ensure ambient conditions are accounted for, and compare readings with local residential noise regulations.


