Corrosion Testing Methods
Corrosion, the gradual degradation of materials or metals due to chemical reactions with their environment, poses significant challenges in industries ranging from infrastructure and manufacturing to transportation and energy. To ensure the longevity and reliability of materials, it is essential to employ rigorous corrosion testing methods.
These methods enable engineers and scientists to assess the resistance of materials to corrosion, identify potential vulnerabilities, and develop effective strategies to mitigate corrosion-related risks. In this article, we will delve into the world of corrosion testing methods, exploring some commonly used techniques employed across various industries.
Salt Spray Testing
Salt spray testing, also known as the ASTM B117 test, is one of the most prevalent and well-established methods for evaluating corrosion resistance. It aims to simulate the corrosive effects of salt-laden environments, such as coastal regions or areas exposed to de-icing salts. In this test, the material under evaluation is exposed to a controlled mist or fog of saltwater, typically containing sodium chloride, for a specified duration.
The sample’s performance is assessed by observing the formation and progression of corrosion, blistering, or other visible signs of degradation. Salt spray testing provides valuable information on the material’s ability to withstand corrosive environments.
Read more about Salt Spray Testing
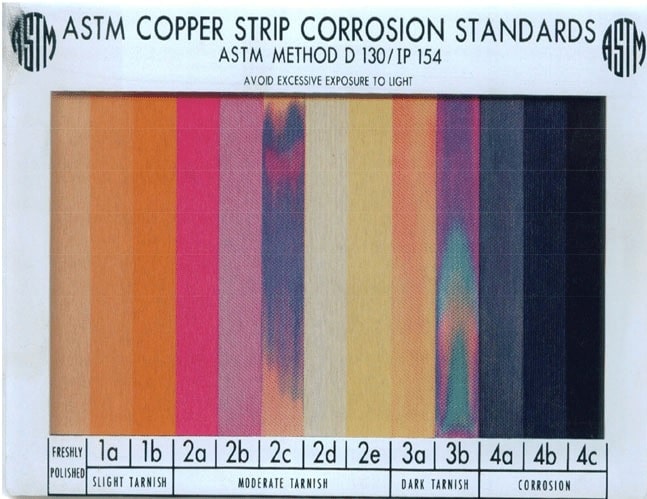
Copper Strip Corrosion Test
The copper strip corrosion test is a widely used method to evaluate the corrosivity of petroleum products containing sulfur compounds. A clean copper strip is immersed in the test sample and subjected to controlled conditions, typically at elevated temperatures. After a specified period, the strip is visually inspected for corrosion or discoloration.
The severity of corrosion observed on the strip provides insight into the potential of the tested product to cause corrosion in practical applications. This simple and cost-effective test aids in quality control, formulation, and material selection, helping industries manage the corrosive effects of petroleum products and ensure the integrity of storage tanks, pipelines, and fuel systems.
Corrosion Coupon Testing
Corrosion coupon testing is a widely used method for assessing and monitoring corrosion in various industries. It involves the exposure of small metal specimens, known as corrosion coupons, to the same environment as the equipment or structure being monitored.
These coupons are then analyzed to evaluate the extent of corrosion, providing valuable data on corrosion rates, characteristics, and the effectiveness of corrosion control measures. By regularly monitoring corrosion coupons, industries can make informed decisions regarding maintenance schedules, material selection, and corrosion mitigation strategies, ultimately ensuring the integrity and longevity of their assets.
Read more about Corrosion Testing Laboratories
Electrochemical Corrosion Testing Methods
Electrochemical corrosion testing methods are widely used for studying the corrosion behavior of materials. These techniques involve measuring the electrical properties of a material immersed in a corrosive solution. Two common electrochemical methods for corrosion testing are potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS).
Potentiodynamic polarization determines the corrosion potential and corrosion rate of a material by measuring its current response to a range of applied potentials. It provides insights into the material’s ability to resist corrosion and helps determine its critical parameters, such as the breakdown potential.
EIS measures the impedance response of a material to an applied sinusoidal electrical signal. By analyzing the frequency-dependent impedance, EIS provides valuable information on the material’s resistance to corrosion, the presence of protective oxide layers, and the kinetics of corrosion processes. EIS is particularly useful for studying the long-term behavior of materials in corrosive environments.
Immersion Testing
Immersion testing involves submerging material samples in corrosive liquids for extended periods. This method allows for the assessment of a material’s susceptibility to corrosion under specific conditions. Immersion testing can be conducted in various corrosive solutions, including saltwater, acidic or alkaline solutions, or chemicals relevant to the intended application. The samples are evaluated by measuring weight loss, surface appearance changes, or alterations in mechanical properties. Immersion testing provides insights into the material’s corrosion resistance and can help identify the most suitable materials for specific environments.
Learn More about Corrosion Control at Data Center
Cyclic Testing
Cyclic corrosion testing is designed to replicate real-world conditions that materials may experience throughout their service life. It exposes samples to cycles of different corrosive atmospheres, temperature changes, humidity variations, and salt spray. By subjecting materials to these cyclic stressors, this method simulates the effects of corrosion fatigue, thermal cycling, and exposure to environmental pollutants. Cyclic testing provides a comprehensive evaluation of a material’s resistance to degradation mechanisms such as cracking, pitting, or general corrosion.
Corrosion Testing Methods for Metals
Metals are susceptible to corrosion due to their reaction with environmental factors like moisture, oxygen, and chemicals. Various corrosion testing methods for metals are used to assess their resistance to degradation under specific conditions.
One of the most common methods is the salt spray test (ASTM B117), where metal specimens are exposed to a saline mist in a controlled chamber to simulate harsh environments. Another effective technique is electrochemical testing, including potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), which measure corrosion rates and resistance. Immersion tests involve submerging metal samples in corrosive solutions to study material behavior over time.
High-temperature oxidation tests assess metal performance under extreme heat, while cyclic corrosion testing simulates real-world exposure by alternating wet and dry conditions. Galvanic corrosion testing examines the interaction between different metals in contact, ensuring compatibility in applications like marine structures and pipelines. Standard organizations like ASTM, ISO, and NACE provide detailed procedures to ensure accuracy and reproducibility. Understanding these corrosion testing methods helps industries select appropriate materials and coatings, improving the durability of structures, machinery, and automotive components against corrosion-related failures.
Accelerated Testing
Accelerated corrosion testing methods aim to simulate the effects of long-term exposure to corrosive environments within a shorter timeframe. These tests employ accelerated conditions, such as elevated temperature, increased humidity, or higher concentrations of corrosive agents, to expedite the corrosion process. Accelerated testing methods, including salt fog testing, cyclic wet and dry exposure, or high-temperature exposure, provide faster results compared to natural or real-time testing. However, caution must be exercised when interpreting the results, as accelerated testing may not perfectly replicate real-world conditions.
Crevice Corrosion Testing
Crevice corrosion is a localized form of corrosion that occurs in confined spaces, such as gaps, joints, or under deposits, where stagnant conditions can promote corrosion initiation and propagation. Testing methods for crevice corrosion involve creating artificial crevices or using crevice-forming devices in the sample setup. These tests evaluate the material’s susceptibility to crevice corrosion by monitoring the corrosion initiation and propagation within these confined spaces. Crevice corrosion testing is essential, particularly in industries where materials are subjected to environments with potential crevices or gaps, such as offshore structures or piping systems.
Perfect Pollucon Services offers Corrosion Testing Services. Contact us now for more information.
Galvanic Corrosion Test Methods
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact within an electrolyte, leading to accelerated corrosion of the more active metal. Galvanic corrosion test methods evaluate the compatibility of different metals in real-world applications, such as marine environments, pipelines, and structural assemblies.
One common test is the galvanic couple test, where paired metal samples are immersed in a corrosive medium while measuring potential differences and corrosion rates. Electrochemical methods like potentiostatic and galvanic current measurements help assess corrosion behavior under controlled conditions.
Salt spray testing (ASTM B117) can also be used to evaluate galvanic corrosion in atmospheric conditions. Immersion tests expose metal combinations to various electrolytes, such as seawater or acidic solutions, to analyze degradation patterns.
Engineers use these tests to select materials that minimize galvanic corrosion risks by incorporating insulating barriers, protective coatings, or sacrificial anodes. Understanding and testing for galvanic corrosion is essential in industries like marine, aerospace, construction, and automotive, where material longevity is critical for safety and performance.
Corrosion Test on Steel
Steel is widely used in construction, transportation, and industrial applications, making corrosion resistance a crucial factor. A corrosion test on steel assesses how different grades of steel react to moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations. Salt spray testing (ASTM B117) is a common method for evaluating coated and uncoated steel by exposing it to a saline mist.
Electrochemical corrosion tests, such as potentiodynamic polarization and impedance spectroscopy, provide insights into steel’s corrosion rate and protective coating efficiency. Atmospheric corrosion tests simulate real-world conditions by exposing steel samples to controlled humidity, pollutants, and temperature cycles.
Immersion tests assess steel performance in acidic, alkaline, or marine environments. High-temperature oxidation tests determine steel durability in extreme heat applications like power plants and aerospace components.
Engineers use these tests to develop corrosion-resistant alloys, coatings, and inhibitors, ensuring long-term performance and structural integrity in demanding environments.
Corrosion Testing Machine
A corrosion testing machine is an advanced laboratory instrument designed to simulate real-world corrosive environments and measure material degradation. These machines come in various forms, each tailored for specific testing methods. The salt spray chamber, widely used in ASTM B117 and ISO 9227 tests, exposes samples to a continuous salt mist to accelerate corrosion.
Electrochemical corrosion testers, equipped with potentiostats and galvanostats, analyze corrosion rates through techniques like potentiodynamic polarization and EIS. Cyclic corrosion testers simulate natural environmental conditions by alternating between wet, dry, and humid phases to evaluate coatings and metals under realistic exposure conditions.
Some corrosion testing machines are designed for high-temperature oxidation tests, used in aerospace and power plant industries. Modern machines incorporate automated data logging, real-time monitoring, and programmable settings, ensuring precise and repeatable results.
Many industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and marine, rely on corrosion testing machines to validate material performance, develop protective coatings, and meet international corrosion standards. Investing in high-quality corrosion testing machines enhances research efficiency, reduces material failures, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Importance of Corrosion Testing Methods
Corrosion testing methods play a vital role in ensuring the durability and reliability of materials in numerous industries. By subjecting materials to controlled corrosive environments and evaluating their performance using a range of testing methods, engineers and scientists can identify potential vulnerabilities, develop effective corrosion mitigation strategies, and select appropriate materials for specific applications. From salt spray testing to electrochemical methods, immersion testing, cyclic testing, accelerated testing, and crevice corrosion testing, each method provides unique insights into the corrosion behavior of materials. The selection of appropriate testing methods depends on the specific requirements of the industry, the intended application, and the environmental conditions the materials will encounter. Through thorough corrosion testing, manufacturers can enhance the corrosion resistance of materials, leading to increased safety, reduced maintenance costs, and improved overall performance in a wide range of applications.
Purpose of Corrosion Testing?
The purpose of corrosion testing is to assess and evaluate the behavior of materials and structures in corrosive environments. It helps in understanding the corrosion mechanisms, rates, and types of corrosion occurring.
The data obtained from corrosion testing is used for material selection, design optimization, quality control, and the development of effective corrosion prevention and mitigation strategies. By conducting corrosion testing, industries can ensure the longevity and reliability of their assets, reduce maintenance costs, comply with regulatory requirements, and enhance safety.
Overall, corrosion testing plays a critical role in managing and mitigating the damaging effects of corrosion, enabling industries to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect their infrastructure and equipment.

Anil Shelke is the Executive Director at Perfect Pollucon Services with 30+ years of expertise in pollution control, environmental audits, hazardous waste management, and ISO 14001 implementation. He specializes in helping industries align with CPCB/SPCB regulations.
Corrosion testing methods include salt spray testing, electrochemical testing, immersion testing, and cyclic corrosion testing to evaluate material durability. These tests help assess corrosion resistance in different environmental conditions.
The three primary methods of corrosion are uniform corrosion (even surface attack), pitting corrosion (localized small holes), and galvanic corrosion (metal interaction with another metal). Each method requires specific prevention strategies.
Corrosion can be detected using visual inspection (rust or discoloration), ultrasonic testing (measuring material thickness loss), and electrochemical techniques (monitoring corrosion rates through current measurements). These methods help assess material degradation.
A corrosion test is conducted by exposing materials to corrosive conditions such as salt spray, humidity, or acidic environments and measuring weight loss, surface degradation, or electrochemical response over time.
ISO 11463 outlines the standard for evaluating pitting corrosion using visual and electrochemical techniques to quantify pit depth and density.
Corrosion types include uniform corrosion, pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, intergranular corrosion, stress corrosion cracking, and galvanic corrosion. Each type occurs under specific environmental conditions.
Corrosion occurs due to electrochemical reactions where metals lose electrons to oxygen and moisture, forming oxides or other compounds. This process degrades metal strength over time.
The chemical formula for rust is Fe₂O₃·xH₂O, representing hydrated iron(III) oxide, which forms when iron reacts with oxygen and water.
Lower pH (acidic) environments accelerate corrosion, while higher pH (alkaline) environments slow it down by reducing the availability of hydrogen ions that promote metal dissolution.
Rust testing involves exposing metal to moisture, chloride solutions, or salt spray chambers and assessing surface oxidation, weight loss, or color change over time.
Corrosion analysis involves identifying the type, cause, and rate of corrosion using laboratory tests, microscopy, and electrochemical measurements to develop preventive solutions.
Pitting is a localized form of corrosion that creates small holes or cavities on metal surfaces, often caused by chloride ions or oxygen concentration differences.
The corrosion rate formula is CR = (K × Weight Loss) / (Density × Surface Area × Time), where K is a conversion factor based on the units used.
Corrosion monitoring methods include electrochemical sensors, weight loss coupons, ultrasonic thickness measurements, and real-time corrosion probes to assess material degradation.
Corrosion inhibitor testing includes electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), potentiodynamic polarization, and weight loss measurements to evaluate the effectiveness of inhibitors.
Corrosion can be prevented by painting/coating (creating a barrier), galvanization (zinc coating), and cathodic protection (sacrificial metal anodes). These methods extend the lifespan of metals.
The primary agents of corrosion are oxygen (oxidation reactions), moisture (water accelerates corrosion), and acidic substances (low pH environments enhance metal degradation).
Steel can be protected by applying protective coatings (paint, powder coating), using corrosion-resistant alloys (stainless steel), and employing cathodic protection (sacrificial anodes).
Corrosion requires a metal surface, an electrolyte (moisture or conductive solution), and an oxidizing agent (oxygen or acids) to initiate and sustain the corrosion process.

