Ambient Air Sampling Methods
Air pollutants are substances present in the atmosphere at concentrations harmful to the environment, living organisms, or humans. The process of sampling and analyzing these pollutants is known as Air Quality Monitoring, a critical component of environmental management. Advanced ambient air sampling methods enable accurate assessment of air quality, helping organizations and individuals make informed decisions for a healthier environment.
Ambient air quality monitoring is crucial for assessing pollution levels and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards set by the CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board). Various industries, municipalities, and research organizations rely on accurate air sampling methods to monitor pollutants and assess environmental impact.
With over 25 years of expertise in air quality assessment, Perfect Pollucon Services has worked with industries, government bodies, and environmental agencies across India to implement effective air sampling strategies, ensuring reliable data collection and compliance with air quality standards.
Understanding the right air sampling methods is essential for detecting pollution trends, assessing health impacts, and maintaining environmental sustainability.
What is Ambient Air Sampling
Ambient air sampling involves collecting air samples from the environment to assess air quality and pollutant levels. This process uses strategically placed sampling devices to capture representative samples, which are analyzed to measure pollutants like particulate matter, gases, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
The data from ambient air sampling helps:
- Assess air quality.
- Identify sources of pollution.
- Monitor compliance with air quality standards.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of pollution control measures.
This practice is essential for understanding air pollution’s impact on human health and the environment. The insights gained are often used by environmental consultants to recommend actions to reduce pollutants to acceptable limits.

Read More About How to reduce Particulate Matter?
Objectives of Air Sampling
The primary objective of air sampling is to collect genuine and representative samples to determine the concentration of gaseous and particulate pollutants. These concentrations are often expressed in milligrams per cubic meter of air. For particulate sampling, high-volume air samplers and dust samplers are commonly used, capturing particles smaller than 10 microns using filtration methods.
Example:
The difference in the weights of filter paper before and after sampling, divided by the quantity of air passed, gives the concentration of particulate matter in the air.
For gaseous sampling, pollutant gases are collected using specialized methods categorized below.
Importance of Air Sampling
AiAir sampling is essential for more than just regulatory compliance. It helps:
- Identify pollutants: Measure particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), VOCs, SO₂, NOₓ, CO, and more.
- Assess health risks: Evaluate exposure levels in workplaces and urban areas.
- Implement control measures: Provide actionable data to design strategies for pollution control.
Businesses, industries, and environmental bodies rely on air sampling to maintain compliance and minimize risks. Perfect Pollucon Services offers comprehensive solutions for all air quality testing needs.
Perfect Pollucon Services has conducted extensive ambient air quality monitoring across industrial zones, urban areas, and high-pollution regions. Over the years, we have observed key challenges industries and municipalities face in maintaining air quality compliance:
- Inconsistent monitoring schedules, leading to incomplete pollution trend analysis.
- Improper placement of air samplers, which skews data accuracy.
- Failure to consider microclimate effects, affecting air quality interpretation.
- Incorrect calibration of sampling equipment, leading to unreliable readings.
Real-World Insight: In one of our projects, an industrial cluster was consistently exceeding particulate matter (PM10 & PM2.5) limits but was unaware of the source. Through strategic ambient air sampling and source identification, we helped them implement better emission control measures, reducing PM levels by 30% in six months.
Common Ambient Air Sampling Methods
Ambient air sampling methods can be broadly categorized into two types: active sampling and passive sampling. Let’s take a closer look at each.
How To Collect Air Samples?
Air samples are collected using various methods depending on the type of pollutants being measured. Active sampling involves using pumps to draw air through filters, sorbent tubes, or impingers, capturing particulates or gases for laboratory analysis. Passive sampling relies on diffusion, where air pollutants accumulate on a collection medium over time.
Real-time monitoring uses sensor-based instruments like dust meters, VOC analyzers, and gas detectors to provide instant readings. For biological contaminants like mold and bacteria, bioaerosol samplers are used. Proper site selection, sample duration, and calibration of instruments are crucial for accurate results in air quality assessments.
Active Sampling Methods
Active sampling requires mechanical devices or pumps to collect air samples, making it highly precise and effective for short-term monitoring.
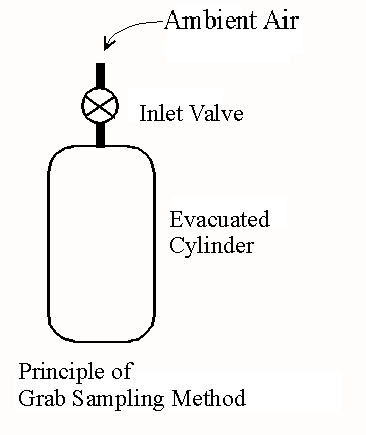
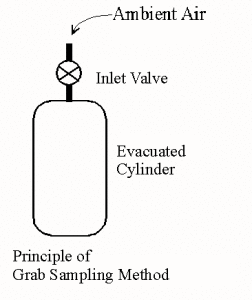
- Grab Sampling
- Description: A simple method where air is collected in an evacuated flask or plastic bag.
- Applications: Used for short-term pollutant analysis.
- Procedure: The container is evacuated or filled with water and replaced with air. The sample is analyzed for pollutants.
- Absorption in Liquids
- Description: Gaseous pollutants are absorbed into a liquid medium (e.g., NaOH solution) for analysis.
- Devices Used: Impingers and midget devices.
- Applications: Popular among environmental consultants due to negligible pollutant loss during sample transport.
- Adsorption on Solids
- Description: Air is passed through a column packed with adsorbent materials like activated charcoal or silica gel, which retain the pollutants.
- Procedure: Pollutants are desorbed using solvents in a lab for further analysis.
- Freeze-Out Sampling
- Description: Air pollutants are condensed using a series of cold traps.
- Applications: Allows detailed analysis using mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, or spectrophotometry.
- Impingement Method
- Description: Air is passed through a liquid medium, where particles and microorganisms are entrapped for analysis.
- Applications: Ideal for microbial air sampling in healthcare and laboratory environments.
Grab Sampling:
Passive Sampling Methods
Passive sampling relies on the natural movement of air without mechanical devices. It is cost-effective and ideal for long-term monitoring.
- Diffusion Tubes
- Description: Pollutants diffuse naturally into a chemical coating within the tube.
- Applications: Best for monitoring nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and ozone (O₃) over time.
- Settling Plate Method (Sedimentation)
- Description: Airborne particles settle onto a collection surface due to gravity.
- Applications: Effective for indoor air quality assessment of larger particles.
- Badge Samplers
- Description: Small, wearable samplers designed to collect air pollutants passively.
- Applications: Commonly used in occupational exposure monitoring.
Air Sampling Techniques
Air sampling techniques are essential for detecting pollutants in indoor and outdoor environments. These techniques include active sampling, where air is drawn through a filter or chemical medium using a pump, and passive sampling, which relies on natural diffusion to collect contaminants over time.
Gravimetric analysis measures particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), while gas chromatography identifies volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Real-time monitoring with sensor-based devices provides instant pollutant readings.
High-volume samplers capture large air samples for laboratory testing, while bioaerosol sampling detects mold and allergens. These methods help assess air quality, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and public health safety.
Air Sampling Methods in Microbiology
In microbiology, air sampling methods are used to assess the presence of microorganisms in the air and evaluate indoor air quality. Some common air sampling methods in microbiology include:
- Impaction Method: This method involves drawing a known volume of air through a collection device, such as an agar plate or a filter. Microorganisms present in the air impact onto the collection surface, where they can grow as colonies on the agar or be quantified through subsequent analysis.
- Impingement Method: In this method, air is drawn through a liquid medium, usually sterile broth, in an impinger device. Microorganisms in the air become entrapped in the liquid, allowing subsequent analysis of the microbial content in the collected liquid.
- Surface Sampling: While not a traditional air sampling method, surface sampling involves swabbing or wiping surfaces to collect settled particles and microorganisms. This method is particularly useful for assessing potential sources of indoor air contamination.
- Filter Method: Air is drawn through a filter, often made of glass fiber or membrane, capturing airborne particles and microorganisms on the filter surface. The filter can then be analyzed to quantify microbial content or identify specific microorganisms.
- Bioaerosol Samplers: These specialized devices are designed to collect airborne particles and microorganisms onto a collection medium. They are commonly used in outdoor and industrial settings.
Microbiological air sampling helps identify potential sources of contamination, monitor cleanrooms, healthcare facilities, and laboratories, and assess the risk of airborne pathogens in various environments. The choice of method depends on the specific objectives of the study, the types of microorganisms being targeted, and the characteristics of the sampling area.
Common Mistakes in Ambient Air Sampling
Through decades of experience in air quality monitoring, Perfect Pollucon Services has identified the most common mistakes industries and municipalities make in ambient air sampling:
🔹 Using incorrect sampling duration – Many organizations conduct short-term sampling, missing out on long-term pollution trends.
🔹 Incorrect placement of sampling stations – Locating samplers too close to pollution sources or too far from affected areas leads to misleading results.
🔹 Failing to monitor all key pollutants – Some industries only measure particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5) while neglecting gaseous pollutants like NO₂, SO₂, and VOCs.
🔹 Lack of proper calibration and maintenance – Faulty or poorly maintained samplers lead to inaccurate readings and unreliable reports.
🔹 Non-compliance with CPCB guidelines – Inadequate sampling frequency and improper methodologies result in regulatory violations and penalties.
By addressing these issues, Perfect Pollucon Services ensures industries and municipalities get accurate air quality data, enabling them to take corrective measures effectively.
Air Sampling Equipment: Tools for Accurate Air Quality Analysis
Proper air sampling equipment is essential for assessing air quality, identifying pollutants, and ensuring a healthy environment. Whether you are monitoring indoor air quality, conducting industrial emissions testing, or researching ambient air conditions, having the right tools is key. Below, we explore some commonly used air sampling equipment and their applications.
1. High-Volume Air Samplers
- Purpose: Collect particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5) for detailed analysis.
- Applications: Widely used for environmental monitoring and regulatory compliance.
2. Impingers
- Purpose: Capture gaseous pollutants by bubbling air through a liquid medium.
- Applications: Ideal for measuring sulfur dioxide (SO₂), ammonia, and other gases.
3. Adsorption Tubes
- Purpose: Trap volatile organic compounds (VOCs) using materials like activated carbon or silica gel.
- Applications: Commonly used in industrial settings to monitor hydrocarbons and organic vapors.
4. Diffusion Tubes
- Purpose: Passively collect air pollutants through natural diffusion.
- Applications: Great for long-term monitoring of nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and ozone (O₃).
5. Real-Time Air Monitors
- Purpose: Provide immediate data on air quality, including particulate concentration and gas levels.
- Applications: Used in research, occupational health monitoring, and urban air quality studies.
Why Choose the Right Air Sampling Equipment?
Using the appropriate air sampling equipment ensures accuracy, compliance with environmental standards, and actionable insights into air quality. Whether you’re conducting workplace safety assessments or regional pollution studies, the right tools can make a significant difference.
For comprehensive air quality testing solutions, consider Perfect Pollucon Services. With state-of-the-art equipment and expert guidance, we help you achieve reliable results to protect health and the environment.
Selection of Air Sampling Location
Choosing the right sampling locations is critical for effective air quality monitoring. Factors like proximity to emission sources, wind direction, and human activity influence location selection.
High-risk areas, such as industrial zones and busy intersections, should be prioritized for a comprehensive evaluation.
Air Sampling Methods PDF
Air sampling methods are essential for monitoring and analyzing the quality of air in various environments. From industrial workplaces to urban settings, these methods help identify pollutants such as particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and gases like CO, SO₂, and NOₓ. Techniques such as active sampling with filtration or adsorption and passive sampling using diffusion tubes or badge samplers provide reliable insights into air quality. This downloadable PDF offers a comprehensive overview of air sampling methods, their applications, and how they contribute to health and environmental safety. Perfect for environmental professionals and researchers.
Download Air sampling methods PDF here:
Let us know your views on this post.
Learnings from 25 Years of Air Quality Monitoring
With over 25 years of experience in ambient air quality monitoring, Perfect Pollucon Services has observed key trends:
✅ Industries that conduct periodic air quality assessments see a 40% improvement in pollution control measures.
✅ Implementing real-time air monitoring leads to faster detection and response to pollution spikes.
✅ Proper placement of air samplers improves accuracy by 30-50%, ensuring reliable pollution trend analysis.
✅ Advanced sampling techniques, such as high-volume samplers and passive diffusion samplers, provide more comprehensive pollutant profiling.By leveraging our expertise, Perfect Pollucon Services ensures that industries, regulatory agencies, and research institutions collect precise air quality data to drive better environmental policies and pollution control strategies.
Why Choose Perfect Pollucon Services?
Accurate ambient air sampling is critical for ensuring regulatory compliance, understanding pollution sources, and protecting environmental and human health.
With over 25 years of expertise in air quality monitoring, Perfect Pollucon Services has helped industries, municipalities, and environmental agencies implement effective air sampling programs, ensuring compliance with CPCB standards and improving overall air quality.
👉 Need professional ambient air sampling and compliance support? Contact us today for a customized air quality monitoring solution.
Know More about Environmental Monitoring
Learn more aboutEnvironmental monitoring Methods

Kunal Gajare is an Environmental Engineer with a B.E. in Chemical Engineering and M.E. in Environmental Engineering. With 10+ years of experience, he leads projects in environmental clearances, EIA, MPCB compliance, and sustainable pollution control practices.
Ambient air sampling collects air samples from the surrounding environment to assess overall air quality, while stack sampling collects air samples from specific emission sources such as industrial stacks to measure pollutant concentrations and compliance with regulations.
The two types of air sampling are active sampling and passive sampling. Active sampling uses mechanical devices or pumps to draw air through a collection medium, while passive sampling relies on natural air movement to diffuse pollutants onto a sorbent material or collection surface.
Air sampling is typically conducted using air sampling pumps, which draw air through filters or collection media to capture airborne particles and contaminants. These collected samples can then be analyzed in laboratories to assess air quality, identify pollutants, and determine potential health risks.
There are several types of air sampling methods used to assess air quality and detect pollutants. These include grab sampling, where air is collected at a specific moment; passive sampling, which uses devices like diffusion tubes to capture pollutants over time; and active sampling, involving the use of pumps to actively draw air through filters or sorbent media. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific pollutants being targeted and the monitoring objectives.
Air sampling is collected using various methods. For grab sampling, an air sample is quickly collected at a specific location and time using a handheld device. Passive sampling involves leaving devices like diffusion tubes in the sampling area to accumulate pollutants over a certain period. Active sampling employs pumps to actively draw air through filters or sorbent media, allowing for precise control over the sampling rate and volume.
Air sampling for microbiology typically employs two main methods: impaction and impingement. Impaction involves drawing air through a sampler where particles impact onto an agar plate, allowing microbial colonies to grow. Impingement uses a liquid medium to capture microorganisms from the air, with the collected liquid subsequently analyzed for microbial content. These methods help assess indoor air quality, identify potential pathogens, and monitor microbial contamination in various settings.
An air sampling system is a setup of devices and techniques used to collect and analyze air samples to measure the concentration of pollutants such as gases, particulate matter, and microorganisms. It helps assess air quality, identify pollution sources, and ensure compliance with environmental and health standards.
The objective of air sampling is to collect representative air samples to measure pollutant concentrations, assess air quality, and evaluate health or environmental risks. This data aids in pollution control, regulatory compliance, and ensuring a safe environment.
The working principle of an air sampler involves drawing a specific volume of air through a collection medium (such as a filter, liquid, or adsorbent) using a pump or natural diffusion. As air passes through, pollutants like particulate matter, gases, or microorganisms are captured on the medium for subsequent analysis, enabling the measurement of pollutant concentrations and air quality.
To take a sample of air, you use an air sampler, which draws air through a collection medium such as a filter, liquid, or adsorbent. The collected sample is then analyzed to measure the concentration of pollutants like particulate matter, gases, or microorganisms.
An air sampling point is a specific location where air samples are collected to monitor and analyze air quality. It is strategically chosen based on factors like proximity to pollution sources, wind direction, and the area’s environmental or health concerns.
The basic principle of air sampling is to collect a representative sample of air using a collection medium (e.g., filters, liquids, or adsorbents) to measure the concentration of pollutants. This process helps assess air quality, identify contaminants, and evaluate health and environmental risks.
Microbes in air are detected using methods like impaction, where air is drawn onto agar plates for microbial growth, or impingement, where air is passed through a liquid medium to trap microorganisms. Advanced techniques like filtration and bioaerosol samplers are also used for analysis through culturing, microscopy, or molecular methods.
We use high-volume samplers, low-volume PM2.5 samplers, passive samplers, and CAAQMS for accurate ambient air quality data, as per CPCB and NAAQS guidelines.
The two main types are active sampling (using pumps/samplers) and passive sampling (diffusion-based), both used by PPS based on pollutant type and monitoring duration.
We test ambient air using calibrated samplers to measure PM10, PM2.5, SO₂, NO₂, and more, then analyze results in NABL-accredited labs per CPCB protocols.
We use gravimetric analysis with low-volume samplers and 47 mm PTFE filters, as per CPCB Method (IS 5182 Part 23) for accurate PM2.5 data.